Infrastructure-level applications
The infrastructure-level applications were copied in from previous iterations of this deployment pattern, customizing where necessary and sometimes improving them.
MetalLB
The config uses the internal static IP 192.168.1.174 identified by the Terraform-generated README file.
ArgoCD
Install ArgoCD using local helm command first:
helm install -n argo-cd --create-namespace argo-cd charts/argo-cd
Login using kubectl port-forward (or cheat using Lens) using the admin credentials.
Push the initial commit of deployment repo with the basic applications defined.
Add the root app manually in the ArgoCD interface:
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: root
spec:
destination:
name: ''
namespace: argo-cd
server: 'https://kubernetes.default.svc'
source:
path: apps/root
repoURL: 'https://gitlab.com/spt3g/kubernetes.git'
targetRevision: main
project: spt3g
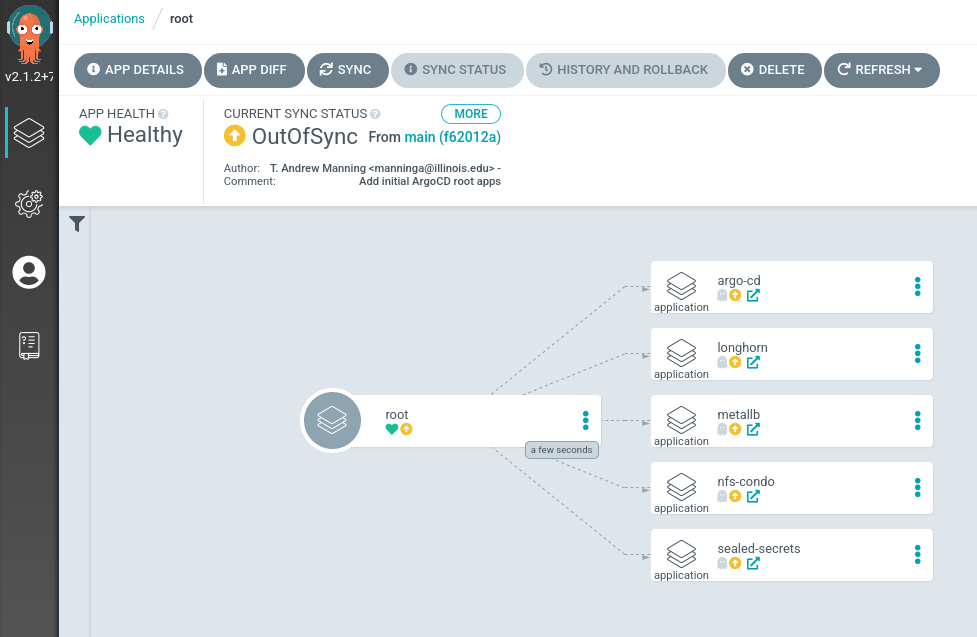
Sync each app.
This fails because the namespaces do not exist yet. Create them:
$ kubectl create ns longhorn-system
namespace/longhorn-system created
$ kubectl create ns metallb-system
namespace/metallb-system created
$ kubectl create ns nfs-condo
namespace/nfs-condo created
$ kubectl create ns sealed-secrets
namespace/sealed-secrets created
Sync the apps again.
Create GitLab application via the spt3g group with
Callback: https://argocd.spt3g.ncsa.illinois.edu/api/dex/callback
Confidential: Yes
Scopes:
- read_user (Read the authenticated user's personal information)
- openid (Authenticate using OpenID Connect)
Create a Sealed Secret that includes the existing content of argocd-secret as well as the dex.gitlab.clientId and client secret specified in the ArgoCD deployment for external auth.
Traefik and Certificate Manager
Start with the letsencrypt-staging ClusterIssuer in cert-manager until we get the DNS records and we are certain that certs are being obtained properly. This avoids the rate limiting enforced by LetsEncrypt.
Create the namespaces and then push the commits to the deployment repo and then sync ArgoCD root app.
$ kubectl create ns traefik
namespace/traefik created
$ kubectl create ns cert-manager
namespace/cert-manager created
Keel
Keel is a Kubernetes Operator to automate deployment updates. By applying annotations to Deployment objects, Keel will monitor the container image registry for updates to the container image and automatically pull the images and restart the pods as configured. This enables a DevOps workflow in which accepting a pull request to a source code repo is the only action required to update a running service, assuming that there is a GitLab CI/CD pipeline or GitHub Action configured to automatically trigger upon commit an image rebuild and push to the container registry.
Create an access token for Keel to use to read the container registry using scope read_api.
Use this token to log in to the registry using your GitLab username:
$ docker login registry.gitlab.com/spt3g/kubernetes --username ${GITLAB_USERNAME}
Password:
WARNING! Your password will be stored unencrypted in /home/manninga/.docker/config.json.
Configure a credential helper to remove this warning. See
https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/commandline/login/#credentials-store
Login Succeeded
View the contents of $HOME/.docker/config.json and extract the relevant auth:
$ cat ~/.docker/config.json
{
"auths": {
"registry.gitlab.com": {
"auth": "*****"
}
}
}
Construct a YAML file scripts/secret_generator/secrets/spt3g-secrets.yaml to include this secret:
secrets:
- name: argocd-secret
data: |
dex.gitlab.clientId: *****
dex.gitlab.clientSecret: *****
admin.password: *****
admin.passwordMtime: *****
server.secretkey: *****
- name: gitlab-read-api
data: |
.dockerconfigjson: |
{
"auths": {
"registry.gitlab.com": {
"auth": "*****"
}
}
}
Run the Sealed Secret generator script
cd scripts/secret_generator
python3 seal_bulk_secrets.py --file secrets/spt3g-secrets.yaml
Copy the contents of scripts/secret_generator/sealed-secrets/sealed.gitlab-read-api.secret.yaml into charts/keel/templates/secrets.yaml.
Create the namespace, commit the ArgoCD Application manifest and keel Helm chart and sync ArgoCD root app.
$ kubectl create ns keel
namespace/keel created
Longhorn
Open the web UI served from the longhorn-ui deployment by using kubectl port-forward and opening a browser to http://127.0.0.1:8000.
$ kubectl port-forward -n longhorn-system svc/longhorn-frontend 8000:80
Forwarding from 127.0.0.1:8000 -> 8000
Forwarding from [::1]:8000 -> 8000
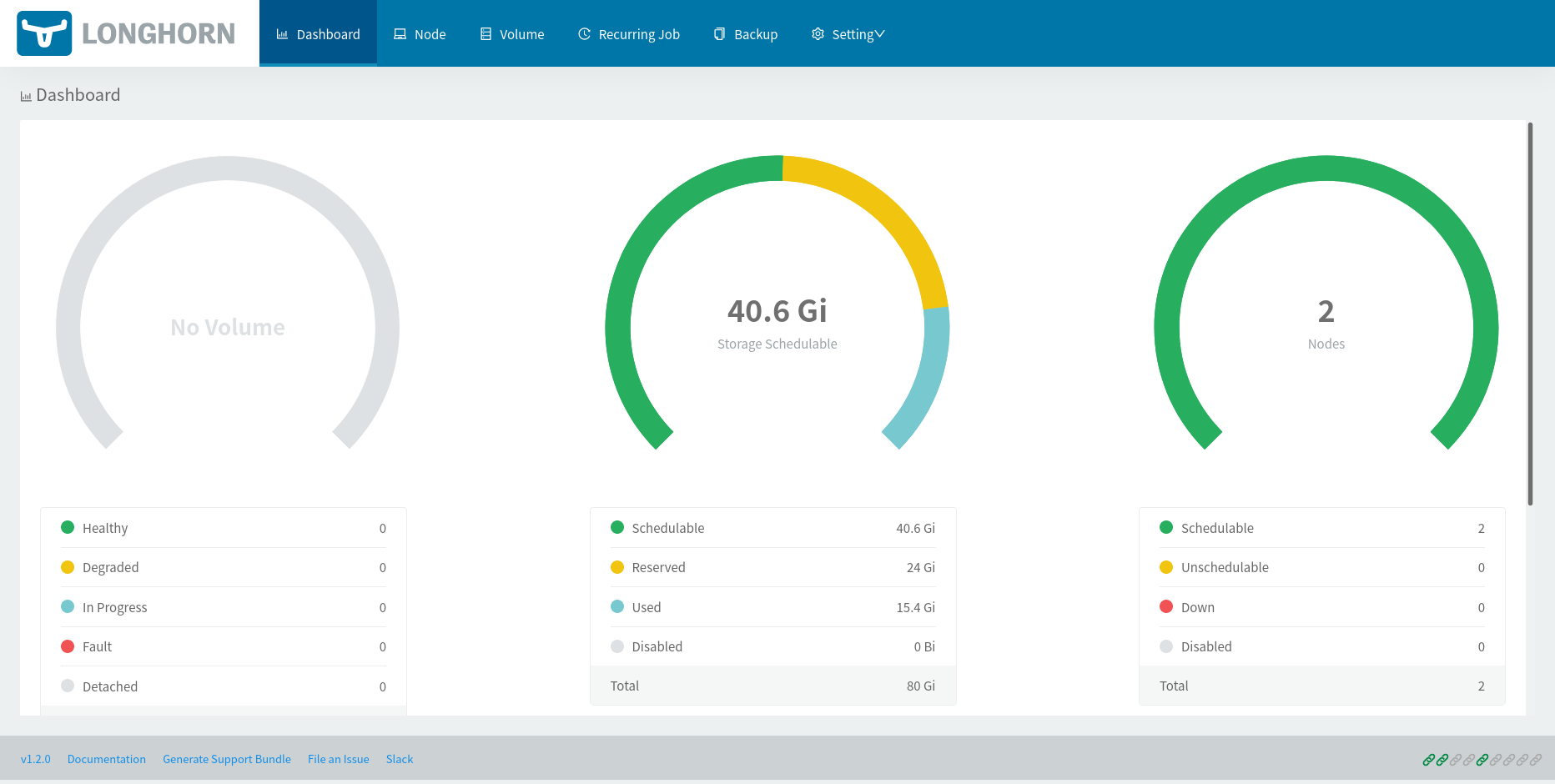
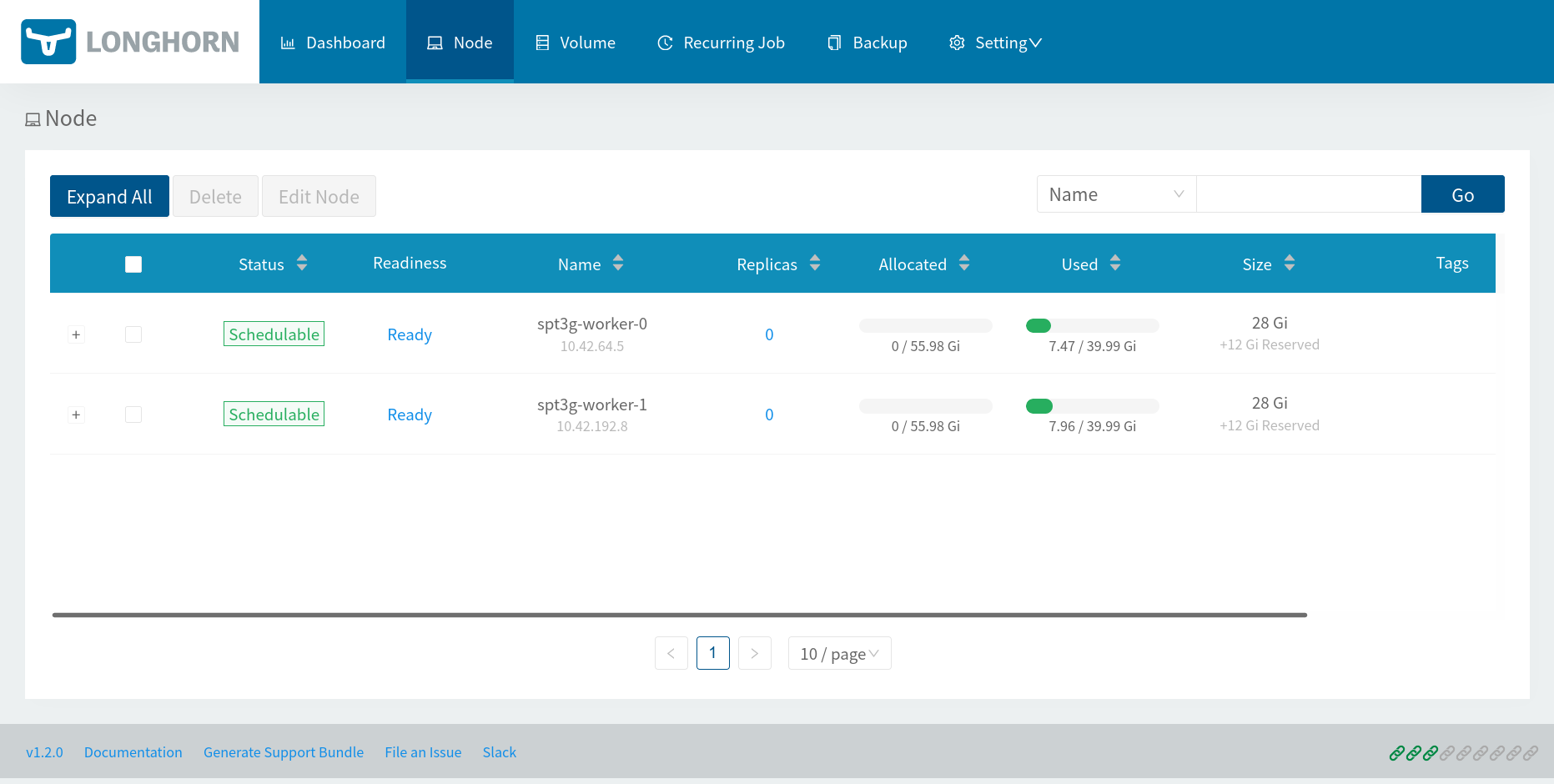
Sealed Secrets
Sealed Secrets are a “one-way” encrypted Secret that can be created by anyone, but can only be decrypted by the controller running in the target cluster. The Sealed Secret is safe to share publicly, upload to git repositories, post to twitter, etc. Once the SealedSecret is safely uploaded to the target Kubernetes cluster, the sealed secrets controller will decrypt it and recover the original Secret.
How to create sealed secrets
We use a custom script to make generating sealed secrets more convenient. First, construct a YAML file scripts/secret_generator/secrets/spt3g-secrets.yaml where secrets are specified in plaintext following this example:
secrets:
- name: argocd-secret
data: |
dex.gitlab.clientId: *****
dex.gitlab.clientSecret: *****
admin.password: *****
admin.passwordMtime: *****
server.secretkey: *****
- name: gitlab-read-api
data: |
.dockerconfigjson: |
{
"auths": {
"registry.gitlab.com": {
"auth": "*****"
}
}
}
Run the Sealed Secret generator script
cd scripts/secret_generator
python3 seal_bulk_secrets.py --file secrets/spt3g-secrets.yaml
Copy the contents of the desired secret into the Helm chart secrets.yaml template file. For example, if the keel chart needs a secret gitlab-read-api, then append the YAML content of scripts/secret_generator/sealed-secrets/sealed.gitlab-read-api.secret.yaml to charts/keel/templates/secrets.yaml:
---
apiVersion: bitnami.com/v1alpha1
kind: SealedSecret
metadata:
annotations:
sealedsecrets.bitnami.com/cluster-wide: "true"
creationTimestamp: null
name: gitlab-read-api
spec:
encryptedData:
.dockerconfigjson: AgB...+pq1A=
template:
data: null
metadata:
annotations:
sealedsecrets.bitnami.com/cluster-wide: "true"
creationTimestamp: null
name: gitlab-read-api
type: Opaque
Master key backup
The master key required to decrypt the Sealed Secrets was downloaded for backup purposes following the documentation here:
kubectl get secret -n sealed-secrets \
-l sealedsecrets.bitnami.com/sealed-secrets-key -o yaml \
>> spt3g-sealed-secrets-master-key.yaml